| Самолеты (сортировка по:) | |||||
| Страна | Конструктор | Название | Год | Фото | Текст |
LVG B.II

|
Страна: Германия Год: 1914
|
| LVG - B.I - 1914 - Германия | <– | –> | LVG - C.I - 1915 - Германия |
 |
J.Herris - LVG Aircraft of WWI. Volume 1: B-Types & C.I /Centennial Perspective/ (34) |
| LVG B.II 654 of an unknown flying school in 1918. |
 |
J.Herris - LVG Aircraft of WWI. Volume 1: B-Types & C.I /Centennial Perspective/ (34) |
| LVG B.II B.715/15 circa 1915/1916. Unit unknown. |
 |
J.Herris - LVG Aircraft of WWI. Volume 1: B-Types & C.I /Centennial Perspective/ (34) |
| LVG B.II(Ot) B.1510/15 of the Bulgarian air service. |
 |
J.Herris - Otto, AGO and BFW Aircraft of WWI /Centennial Perspective/ (37) |
| LVG B.II(Ot) B.1563/15. Unit unknown. |
 |
J.Herris - LVG Aircraft of WWI. Volume 1: B-Types & C.I /Centennial Perspective/ (34) |
| LVG B.II S.97 of the German Naval Air Service. |
 |
J.Herris - LVG Aircraft of WWI. Volume 1: B-Types & C.I /Centennial Perspective/ (34) |
| LVG B.II LA29 of the Netherlands Air Service. B.II 1069/15 landed in Holland on 19 March 1916 and was interned. It was taken in service as LA29. It was armed with a Madsen machine gun fitted outside the aft cabane strut. |
 |
J.Herris - LVG Aircraft of WWI. Volume 1: B-Types & C.I /Centennial Perspective/ (34) |
| Another LVG B.II with no identification numbers visible. (Peter M. Grosz Collection/STDB) |
 |
J.Herris - LVG Aircraft of WWI. Volume 1: B-Types & C.I /Centennial Perspective/ (34) |
| Two photos of a LVG B.II without military serial numbers or flight school numbers visible. (Peter M. Grosz Collection/STDB) |
 |
J.Herris - LVG Aircraft of WWI. Volume 1: B-Types & C.I /Centennial Perspective/ (34) |
| LVG B.II preparing to take off. (Peter M. Grosz Collection/STDB) |
 |
J.Herris - LVG Aircraft of WWI. Volume 1: B-Types & C.I /Centennial Perspective/ (34) |
| LVG B.II running up in the snow for take-off. (Peter M. Grosz Collection/STDB) |
 |
J.Herris - LVG Aircraft of WWI. Volume 1: B-Types & C.I /Centennial Perspective/ (34) |
| LVG B.II trainer at a field in Germany. (Peter M. Grosz Collection/STDB) |
 |
J.Herris - LVG Aircraft of WWI. Volume 1: B-Types & C.I /Centennial Perspective/ (34) |
| LVG B.II trainers lined up at a field in Germany. (Peter M. Grosz Collection/STDB) |
 |
J.Herris - LVG Aircraft of WWI. Volume 1: B-Types & C.I /Centennial Perspective/ (34) |
| LVG B.II trainer taking off from a snowy field in Germany. (Peter M. Grosz Collection/STDB) |
 |
J.Herris - LVG Aircraft of WWI. Volume 1: B-Types & C.I /Centennial Perspective/ (34) |
| LVG B.II trainer of FEA 10 photographed 10 October 1917 by another aircraft from the unit. |
 |
J.Herris - LVG Aircraft of WWI. Volume 1: B-Types & C.I /Centennial Perspective/ (34) |
| Unidentified LVG B.II in flight. (Peter M. Grosz Collection/STDB) |
 |
J.Herris - LVG Aircraft of WWI. Volume 1: B-Types & C.I /Centennial Perspective/ (34) |
| LVG B.II aircraft photographed by FEA I on 15 May 1916. |
 |
J.Herris - LVG Aircraft of WWI. Volume 1: B-Types & C.I /Centennial Perspective/ (34) |
| LVG B.II 534; the location and apparent lack of military serial indicate a civilian trainer. (Peter M. Grosz Collection/STDB) |
 |
J.Herris - LVG Aircraft of WWI. Volume 1: B-Types & C.I /Centennial Perspective/ (34) |
| LVG B.II trainer 654 with 1918 insignia. (Reinhard Zankl) |
 |
J.Herris - LVG Aircraft of WWI. Volume 1: B-Types & C.I /Centennial Perspective/ (34) |
| LVG B.II B.723. The LVG B.II had a cutout in the rear of the upper wing for better field of view for the pilot; the B.I did not have a cutout and that is the key way to distinguish between the two types. (Peter M. Grosz Collection/STDB) |
 |
J.Herris - LVG Aircraft of WWI. Volume 1: B-Types & C.I /Centennial Perspective/ (34) |
| LVG B.II 1510 ready for take-off. (Greg VanWyngarden) |
 |
J.Herris - LVG Aircraft of WWI. Volume 1: B-Types & C.I /Centennial Perspective/ (34) |
| LVG B.II B.916/14 with an unknown pilot. The engine is a 110 hp Benz Bz.II. (Reinhard Zankl) |
 |
J.Herris - LVG Aircraft of WWI. Volume 1: B-Types & C.I /Centennial Perspective/ (34) |
| These photos of LVG B.II 712/15 show how Max Immelmann refitted its machine gun. Two mounts were secured on either side of the observer's cockpit allowing him to reposition it as needed. |
 |
J.Herris - LVG Aircraft of WWI. Volume 1: B-Types & C.I /Centennial Perspective/ (34) |
| LVG B.II B.715/15 in early markings scheme. (Peter M. Grosz Collection/STDB) |
 |
J.Herris - LVG Aircraft of WWI. Volume 1: B-Types & C.I /Centennial Perspective/ (34) |
| LVG B.II 738/15 in flight. (Peter M. Grosz Collection/STDB) |
 |
J.Herris - LVG Aircraft of WWI. Volume 1: B-Types & C.I /Centennial Perspective/ (34) |
| LVG B.II 1038/15 trainer at afield in Germany. (Peter M. Grosz Collection/STDB) |
 |
J.Herris - LVG Aircraft of WWI. Volume 1: B-Types & C.I /Centennial Perspective/ (34) |
| LVG B.II 1048/15. The LVG B.II was a straight-forward development of the robust B.I. The dimensions and weight were reduced somewhat from those of the B.I to improve performance and agility. (Peter M. Grosz Collection/STDB) |
 |
J.Herris - LVG Aircraft of WWI. Volume 1: B-Types & C.I /Centennial Perspective/ (34) |
| Sailors pose with LVG B.ll S.97 assigned to the German Navy. |
 |
J.Herris - LVG Aircraft of WWI. Volume 1: B-Types & C.I /Centennial Perspective/ (34) |
| Otto-built LVG B.II(Ot) |
 |
J.Herris - LVG Aircraft of WWI. Volume 1: B-Types & C.I /Centennial Perspective/ (34) |
| LVG B.II(Ot) 1510/15 is an Otto-built machine at the front. Eight of this type (1503/15-1510/15) were built. It had rails on both sides of the observer's cockpit for mounting a machine gun. (Peter M. Grosz Collection/STDB) |
 |
J.Herris - LVG Aircraft of WWI. Volume 1: B-Types & C.I /Centennial Perspective/ (34) |
| LVG B.II(Ot) B.1563/15 trainer with decorated wheel covers in Germany. (Peter M. Grosz Collection/STDB) |
 |
J.Herris - LVG Aircraft of WWI. Volume 1: B-Types & C.I /Centennial Perspective/ (34) |
| LVG B.IIa(Schul) photographed on 19 February 1918. Was this pristine aircraft a prototype?( Peter M. Grosz Collection/STDB) |
 |
J.Herris - LVG Aircraft of WWI. Volume 1: B-Types & C.I /Centennial Perspective/ (34) |
| The LVG B.II(Schul) was a B.II license-built by Schutte-Lanz, a company better known for building airships. (Peter M. Grosz Collection/STDB) |
 |
J.Herris - LVG Aircraft of WWI. Volume 1: B-Types & C.I /Centennial Perspective/ (34) |
| LVG B.II(Schutte-Lanz) 1397/17 at a flight school in Germany. (Greg VanWyngarden) |
 |
J.Herris - LVG Aircraft of WWI. Volume 1: B-Types & C.I /Centennial Perspective/ (34) |
| Fuselage structure of a LVG B.IIa(Schul). (Peter M. Grosz Collection/STDB) |
 |
J.Herris - LVG Aircraft of WWI. Volume 1: B-Types & C.I /Centennial Perspective/ (34) |
| LVG B.II being used for aerial camera experiments. |
 |
J.Herris - LVG Aircraft of WWI. Volume 1: B-Types & C.I /Centennial Perspective/ (34) |
 |
J.Herris - LVG Aircraft of WWI. Volume 1: B-Types & C.I /Centennial Perspective/ (34) |
| LVG B.II of FFA 6b with an unknown pilot. The engine is a 110 hp Benz Bz.II. (Bruno Schmaling) |
 |
J.Herris - LVG Aircraft of WWI. Volume 1: B-Types & C.I /Centennial Perspective/ (34) |
| Well-maintained LVG B.II with pilot. (Peter M. Grosz Collection/STDB) |
 |
J.Herris - LVG Aircraft of WWI. Volume 1: B-Types & C.I /Centennial Perspective/ (34) |
| LVG B.II fitted with a wireless transmitter for artillery spotting. The radio and antenna are mounted outside of the tight cabin. (Peter M. Grosz Collection/STDB) |
 |
J.Herris - LVG Aircraft of WWI. Volume 1: B-Types & C.I /Centennial Perspective/ (34) |
| An LVG B.II is armed with a captured Lewis gun; the wire attached to the interplane strut prevents the observer from firing into the propeller arc. (Greg VanWyngarden) |
 |
J.Herris - LVG Aircraft of WWI. Volume 1: B-Types & C.I /Centennial Perspective/ (34) |
| Tail of LVG B.IIa (Schul) 237/17 photographed with a student. |
 |
J.Herris - LVG Aircraft of WWI. Volume 1: B-Types & C.I /Centennial Perspective/ (34) |
| LVG B.II and crew of FFA 6b; the aircraft has an early over-engine brow radiator. (Bruno Schmaling) |
 |
J.Herris - LVG Aircraft of WWI. Volume 1: B-Types & C.I /Centennial Perspective/ (34) |
| Franz und Emil review their notes before their next flight in an LVG B.II with early brow radiator. |
 |
J.Herris - LVG Aircraft of WWI. Volume 1: B-Types & C.I /Centennial Perspective/ (34) |
| LVG B.II being photographed. A Madsen gun has been mounted on a gun ring on the observer's cockpit. (Greg VanWyngarden) |
 |
J.Herris - LVG Aircraft of WWI. Volume 1: B-Types & C.I /Centennial Perspective/ (34) |
| LVG B.II aircraft and crew with early Carbonit bomb reproduced as Sanke card 37. |
 |
J.Herris - LVG Aircraft of WWI. Volume 1: B-Types & C.I /Centennial Perspective/ (34) |
| LVG B.II aircraft and crewman with early 5 kg and 10 kg Carbonit bombs. |
 |
J.Herris - LVG Aircraft of WWI. Volume 1: B-Types & C.I /Centennial Perspective/ (34) |
| Armed LVG B.II flown by the Dutch air service as LA29. Only one LVG B.II (later named LA29) was interned in Holland during the war. This was LVG B.II 1069/15 which was interned on 19 March 1916 when it landed at Herpt, Limburg. It had Mercedes #23447. LA29 was the first Dutch airplane with a wireless set. LA29 later became L900 and L800. |
 |
J.Herris - LVG Aircraft of WWI. Volume 1: B-Types & C.I /Centennial Perspective/ (34) |
 |
J.Herris - LVG Aircraft of WWI. Volume 1: B-Types & C.I /Centennial Perspective/ (34) |
 |
J.Herris - LVG Aircraft of WWI. Volume 1: B-Types & C.I /Centennial Perspective/ (34) |
| Armed LVG B.II flown by the Dutch air service; is this also LA29? |
 |
J.Herris - LVG Aircraft of WWI. Volume 1: B-Types & C.I /Centennial Perspective/ (34) |
| LVG B.II in Bulgarian Service. LVG B.II(Ot) 1510/15 is an Otto-built machine at the front. Eight of this type (1503/15-1510/15) were built. It had rails on both sides of the observer's cockpit for mounting a machine gun. |
 |
J.Herris - LVG Aircraft of WWI. Volume 1: B-Types & C.I /Centennial Perspective/ (34) |
| Armed LVG B.II with gun mounting rails for the observer and side radiators. |
 |
J.Herris - LVG Aircraft of WWI. Volume 1: B-Types & C.I /Centennial Perspective/ (34) |
| LVG B.II aircraft in service with the Bulgarian air service. The aircraft feature leading-edge radiators and are armed; mounting rails for machineguns are on both sides of the observer's cockpit. A Madsen machinegun is fitted. |
 |
J.Herris - LVG Aircraft of WWI. Volume 1: B-Types & C.I /Centennial Perspective/ (34) |
 |
J.Herris - LVG Aircraft of WWI. Volume 1: B-Types & C.I /Centennial Perspective/ (34) |
| LVG B.IIa fuselage in the Polish Aviation Museum in Krakow. (Greg Vanwyngarden) |
 |
J.Herris - LVG Aircraft of WWI. Volume 1: B-Types & C.I /Centennial Perspective/ (34) |
| Fuselage restoration. |
 |
J.Herris - LVG Aircraft of WWI. Volume 1: B-Types & C.I /Centennial Perspective/ (34) |
| Top: Tail restoration. Bottom: Engine bearer restoration. |
 |
J.Herris - LVG Aircraft of WWI. Volume 1: B-Types & C.I /Centennial Perspective/ (34) |
| LVG B.IIa Krakow, Poland Museum It is probable that this aircraft, before reaching the Berlin DLS collection, was assembled from the two different machines, the fuselage from a standard production LVG B.II and wings from LVG B.IIa Schutte-Lanz production (S-L Werk Nr 350/17). It would explain different types of markings discovered on this machine, (all photos Piotr Mrozowski) View of the rear cockpit. |
 |
J.Herris - LVG Aircraft of WWI. Volume 1: B-Types & C.I /Centennial Perspective/ (34) |
| View of the rear cockpit. |
 |
J.Herris - LVG Aircraft of WWI. Volume 1: B-Types & C.I /Centennial Perspective/ (34) |
 |
J.Herris - LVG Aircraft of WWI. Volume 1: B-Types & C.I /Centennial Perspective/ (34) |
| ZAK acceptance stamp certifying acceptance of the aircraft after rebuilding. The Preussische Inspektion der Fliegertruppen was one of the German WWI organizations |
 |
А.Александров, Г.Петров - Крылатые пленники России |
| (КПР 10) |
 |
J.Herris - LVG Aircraft of WWI. Volume 1: B-Types & C.I /Centennial Perspective/ (34) |
| LVG B.II S.106 has come to grief; it is assigned to the Navy. |
 |
J.Herris - LVG Aircraft of WWI. Volume 1: B-Types & C.I /Centennial Perspective/ (34) |
| LVG B.II B.1025/15 after a bad landing. (Peter M Grosz Collection/STDB) |
 |
J.Herris - LVG Aircraft of WWI. Volume 1: B-Types & C.I /Centennial Perspective/ (34) |
| LVG B.IIa(Schul) 1392/17 destroyed in a training accident. (Peter M. Grosz Collection/STDB) |
 |
J.Herris - LVG Aircraft of WWI. Volume 1: B-Types & C.I /Centennial Perspective/ (34) |
| LVG B.II 719/15 after a rough landing. (Greg VanWyngarden) |
 |
J.Herris - LVG Aircraft of WWI. Volume 1: B-Types & C.I /Centennial Perspective/ (34) |
| LVG B.II 1039/15 after a bad landing. (Peter M. Grosz Collection/STDB) |
 |
J.Herris - LVG Aircraft of WWI. Volume 1: B-Types & C.I /Centennial Perspective/ (34) |
| LVG B.II(Schutte-Lanz) 1399/17 trainer after a crash. (Greg VanWyngarden) |
 |
J.Herris - LVG Aircraft of WWI. Volume 1: B-Types & C.I /Centennial Perspective/ (34) |
| LVG B.IIa(Schul) 1506/17 destroyed in a training accident. (Peter M. Grosz Collection/STDB) |
 |
J.Herris - LVG Aircraft of WWI. Volume 1: B-Types & C.I /Centennial Perspective/ (34) |
| Remains of LVG B.IIa(Schul) 1530/17 destroyed by fire. (Peter M. Grosz Collection/STDB) |
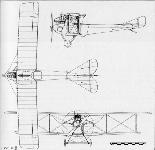 |
O.Thetford, P.Gray - German Aircraft of the First World War /Putnam/ |