L.Opdyke French Aeroplanes Before the Great War (Schiffer)
Deleted by request of (c)Schiffer Publishing
1913: A small fully-covered single-seater with twin skids, nearly vertical and braced from behind: Daucourt used one on 16 April to fly from Buc to Berlin. A 17-rib 2-seater with no cross-axle: Daucourt flew a passenger in one on 30 October from Paris to Cairo.
Jane's All The World Aircraft 1913
BOREL. G. Borel & Cie, 25 rue Brunel, Paris. Established 1910. Capacity: about 25 machines a year.
MODEL 1913 1913 1913
Monoplane Monocoque Racer Hydro-mono.
2-Seater
LENGTH...... 22 feet (6.70 m.) 19 feet (5.80 m.) 27 feet (8.30 m.)
SPAN........ 30 feet (9.15 m.) 26 feet (8.00 m.) 37 feet (11.25 m.)
AREA........ 152 sq.ft.(14 m?.) 116 sq.ft.(11 m?.) 237 sq.ft.(22 m?.)
WEIGHT
....total 530 lbs.(240 kgs.) 608 lbs.(276 kgs.) 880 lbs. (399 kgs.)
....useful 287 lbs.(130 kgs.) ... ...
MOTOR....... 50 Gnome 80 Gnome 80 Gnome
SPEED(p.h.) 71 m. (115 km.) 94 m. (150 km.) 62 m. (100 km.)
Note.--The monocoque is of wood and steel construction, the others wood only. The monocoque has coque body, the others ordinary rectangular section. Floats of the hydro as illustrated. For the rest the ordinary mono. is practically on the same lines as the 1912. The racer is somewhat on Deperdussin lines, but the body is built up inside. No fixed tail. The hydro. is an enlarged edition of the mono. Floats display nothing very original, except that a float under tail is interconnected with the rudder, and that the two front floats are fitted for being rowed. Fitted with a self-starter.
Журнал Flight
Flight, December 13, 1913.
THE STANDS AT THE PARIS AERO SHOW.
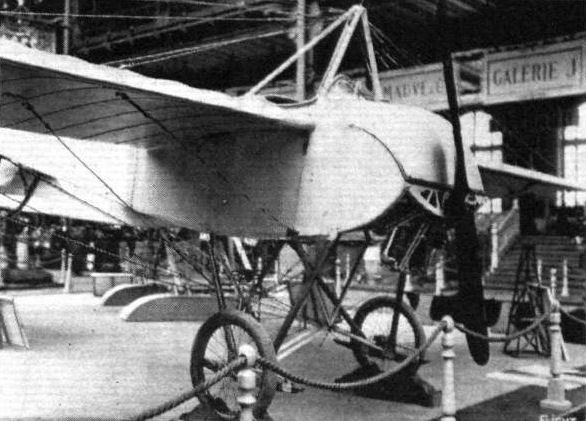
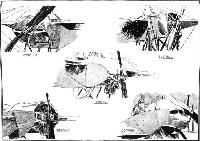
BOREL.
Societe Anonyme des Aeroplanes Borel are represented by three machines. One is a land machine of the military-type tandem two-seater, the pilot occupying the rear seat. A hydro-aeroplane of a similar construction as the land machine, with the exception, of course, that it is fitted with floats instead of wheels, is also shown, but the centre of interest of this stand is undoubtedly the torpedo type of machine on which is mounted a machine gun. In its general appearance this machine is somewhat reminiscent of the Paulhan-Tatin aerial torpedo. The pilot's and passenger's seats are situated in the forward portion of the fuselage, whilst the engine is placed inside the fuselage and behind the passenger's seat, and drives through a long shaft the propeller which is situated at the rear of the fuse/age behind the tail planes. In the nose of the machine is mounted a machine gun (Hotchkiss) which is operated by the passenger.
Flight, December 27, 1913.
THE PARIS AERO SALON - 1913.
BOREL.
Three machines are exhibited on the Borel stand - one military tandem two-seater, a hydro., and the "Ruby." The land machine, which is fitted with a 100 h.p. L.U.C.T. engine of Italian manufacture, is of the standard Borel type. The fuselage is built up of longerons of ash, while the struts and cross-members are ash in front and spruce in the rear portion. The seats are arranged tandem fashion, the pilot occupying the rear seat. The controls are the usual Borel, and may be said to be simply the Bleriot controls without the "cloche." The chassis consists of ash struts carrying two short skids, also of ash, from which are sprung the wheels by means of rubber bands wound round the axle and the skid. The hydro-monoplane is also a tandem two-seater and is similar to those now in use in the Navy. It is driven by an 80 h.p. Gnome engine mounted in front of the fuselage on double bearings, of which the front one can be detached by undoing two bolts, thereby facilitating the operation of removing the engine. The fuselage is exactly similar in construction to that of the land machine. The chassis consists of a structure of streamlined steel tubes, which carry at their lower ends the two main floats. These are pivoted round a transverse tube mounted on the front chassis struts, and are sprung at the rear by means of rubber shock absorbers. Owing to the width of the chassis the angle of the lift wires is extremely good, the inner one being almost vertical.
The pilot's and passenger's seats are arranged tandem fashion, each in a separate cockpit, and the controls are of the usual Borel type. A small float, which turns with the rudder, enables the machine to be steered on the water at slow speeds.
The wings are attached to the fuselage by two bolts passing through the spars, the bolt through the front spar being vertical, while the rear spar bolt is horizontal to allow of the wings being warped without bending the spar. In order to provide a better view in a forward and downward direction, the leading edges have been cut away for a distance of a couple of feet on each side of the fuselage.
<...>