А.Шепс Самолеты Первой мировой войны. Страны Антанты
Эта машина родилась как результат лицензионного производства американскими фирмами европейских самолетов. Ознакомившись с последними британскими и французскими машинами, инженеры фирмы "Воут Корпорейшн" построили легкий многоцелевой самолет для U.S. Navy.
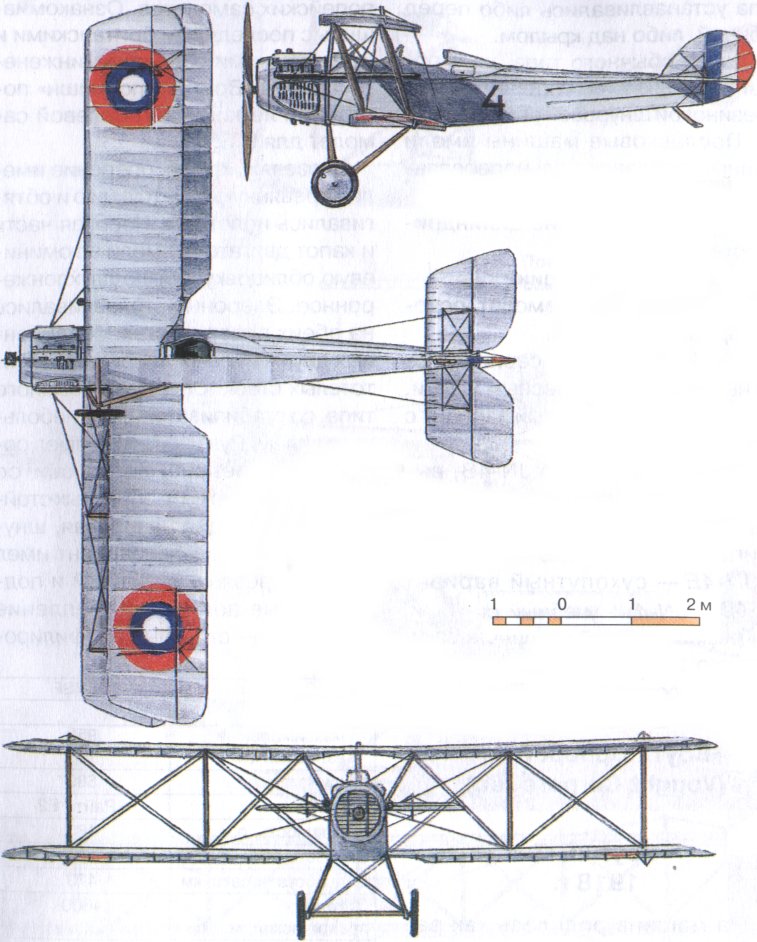
Фюзеляж, крыло, оперение имели деревянную конструкцию и обтягивались полотном. Носовая часть и капот двигателя имели алюминиевую облицовку. Крыло двухлонжеронное. Элероны устанавливались на обеих поверхностях, соединенных двумя парами деревянных пустотелых стоек. Оперение обычного типа, со стабилизаторами и небольшим килем. Руль поворота имел роговую компенсацию. Шасси со сплошной осью на V-образных стойках, амортизация резиновая, шнуровая. Поплавковый вариант имел цельнодеревянные главный и подкрыльевые поплавки. Крепление поплавков - стальные профилированные трубы. Киль поплавковых машин имел значительно большую площадь. В вариантах разведчика, легкого бомбардировщика и истребителя самолет нес вооружение.
Модификации
VE-7 - прототип учебного серийного двухместного самолета.
VE-7G - разведчик и легкий бомбардировщик с тем же двигателем. Вооружение -- 1 синхронный 7,69-мм пулемет "Виккерс" и 1 7,62-мм шкворневый "Льюис". Двигатель мощностью 150л. с.
VE-7S - одноместный истребитель с двумя 7,69-мм пулеметами "Виккерс".
VE-7GF и VE-7SF - развитие машин G и S с более мощным двигателем (180л. с.).
VE-7H - стандартный однопоплавковый разведчики патрульный корабельный самолет.
VE-7SH - одноместный вариант VE-7H.
VE-9 - вариант VE-7 с более мощным двигателем улучшенной аэродинамической формы.
VE-9H - поплавковый вариант VE-9. Двигатель тот же.
Всего построено 128 самолетов VE-7 и 21 VE-9 для U.S. Navy. Эти машины эксплуатировались до 1926 года, a VE-9 - до 1930 года.
Показатель VE-7SF
Размеры, м:
длина 7,45
размах крыльев 10,40
высота 2,62
Площадь крыла, м2 26,43
Вес, кг:
максимальный взлетный 950
пустого 680
Двигатель: "Райт" Е2
мощность, л. с. 180
Скорость, км/ч 188
Дальность полета, км 470
Потолок практический, м 4600
Экипаж, чел. 1
Вооружение 2 пулемета
G.Swanborough, P.Bowers United States Military Aircraft Since 1909 (Putnam)
VOUGHT VE-7, VE-9
The Lewis and Vought VE-7 of 1917 was designed specifically as an advanced trainer, with a 150 h.p. Wright-Hispano “A” engine behind a Spad VII-type radiator. Plans were made for large-scale production, but the demand for advanced trainers was met by converting the Curtiss JN-4 to the Hisso-powered JN-4H, so VE-7 production for the Army was terminated after 14 (inc. 19898/19902) had been delivered by Vought. Two additional improved 180-h.p. models (inc. 40072) were built at McCook Field and four similar models were delivered by Springfield. Two 180-h.p. VE-9 variants (64310, 64316) were procured at the end of the war and an additional 21 (23-379/400) were procured in 1923.
Span, 34 ft. 1 1/2 in.; length, 24 ft. 5 1/2 in.; wing area, 284-5 sq. ft.; empty weight, 1,559 lb.; gross weight, 2,095 lb.; high speed 114 m.p.h.
G.Swanborough, P.Bowers United States Navy Aircraft Since 1911 (Putnam)
Vought VE-7, VE-9
The VE-7, product of the new Lewis & Vought Corporation, appeared in the summer of 1918 after the Aircraft Production Board urged American industry to turn out new original designs for the war programme instead of trying to adapt European designs, as had been the previous policy. Vought was asked to develop an advanced trainer to use the 150hp French Hispano-Suiza Model A engine, then in production by the Simplex Automobile Division of the Wright-Martin Company. (When Wright-Martin broke up, Wright became the Wright Aeronautical Corporation and concentrated its major efforts on engines until merging with Curtiss in 1929 to form Curtiss-Wright. After the war, Lewis & Vought was renamed Chance Vought Corporation after its founder, the famed aircraft designer Chance M. Vought.)
The VE-7 proved to be an excellent design that generally resembled a slightly scaled-down British de Havilland D.H.4 with the nose of a French Spad. Large orders were soon placed, and additional manufacturers were lined up to assist in production. However, the VE-7 did not go into production during the war. This was due to an economy and time-saving measure that resulted in the same 150 hp Wright-Hispano engine being installed in the existing 90 hp Curtiss JN-4D primary trainer, making it the JN-4H for advanced training duties. After the war, the Navy became interested in a version of the VE-7 fitted with the 180 hp Wright-Hispano E engine. The naval versions were built by Vought and by the Naval Aircraft Factory to a total of 128, which was really large-scale production for the early 1920s.
Procured originally for training purposes, the performance of the VE-7 was such that it was used for a great variety of work under a number of sub-designations:
VE-7 - Standard two-seat trainer.
VE-7G - Armed VE-7 with flexible 0.30-in Lewis machine gun in the rear cockpit and a synchronized Vickers gun forward.
VE-7GF - VE-7G with emergency flotation gear.
VE-7H - Trainer or unarmed observation hydroplane (seaplane).
VE-7S - Single-seat fighter with one synchronized Vickers (later Browning) gun.
VE-7SF - VE-7S with flotation gear.
VE-7SH - VE-7S with VE-7H floats.
In the observation models, the observer rode in the forward cockpit, a reversion to early World War I practice when the disposable load of lightweight aircraft was carried right at the centre of gravity. Service experience proved the VE-7s (and later UO-1s) to be notoriously tail-heavy. In spite of its relatively large wingspan, however, the VE-7 made a nimble single-seat fighter, a role in which it served as first-line equipment until 1926, with the pilot occupying the former rear cockpit.
VE-7 landplanes operating over water were frequently fitted with emergency flotation gear of a design developed at the RAF Experimental Station on the Isle of Grain during World War I. Although this feature had been tested on earlier experimental US Navy aircraft, the VE-7s were the first US service models to be so equipped. To prevent nosing over when alighting on water, a Grain-developed hydrovane was installed ahead of the wheels. The seaplane versions were the standard observation and scouting aircraft of the fleet in the early post-war years, being carried aboard battleships and cruisers and launched by catapult. A larger vertical fin was frequently installed on the seaplane versions and was sometimes left in place when the aeroplane was temporarily converted to a landplane.
The VE-9 was identical with the VE-7 except for minor details and the improved E-3 version of the 180 hp Wright-Hispano engine. The Navy ordered 21 as observation models, most being the unarmed VE-9H for use with battleships and cruisers. Two experimental VE-9Ws, to have been fitted with the new 200hp Lawrance J-1 air-cooled radial engine, were cancelled after it was decided to fit the new Vought UO-1 then on order with the radial instead of the higher-powered water-cooled engine for which it had been designed.
TECHNICAL DATA (VE-7SF)
Manufacturer: Lewis & Vought Corporation, Long Island City, NY, and Naval Aircraft Factory, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania.
Type: Fighter.
Accommodation: Pilot only.
Power plant: One 180hp Wright E-2.
Dimensions: Span, 34 ft l3/8 in; length, 24 ft 5 1/8 in; height, 8 ft 7 in; wing area, 284.5 sq ft.
Weights: Empty, 1,505 lb; gross, 2,100 lb.
Performance: Max speed, 117 mph at sea level; climb, 5.5 min to 5,000 ft; service ceiling, 15,000 ft; range, 291 st miles.
Armament: Two fixed forward-firing Vickers 0.303-in or Browning 0.30-in guns.
Serial numbers:
VE-7 (Vought): A5661-A5700; A5912A5941; A6021-A6030.
VE-7 (NAF): A5942-A5969; A5971; A6011-A6020; A6436-A6444.
VE-9 (Vought): A6461-A6481.
VE-9 (NAF): A5970.
Jane's All The World Aircraft 1919
This firm constructs to the designs of Mr. Chance M. Vought, president and chief engineer, a two-seater biplane fitted with a 180 h.p. Hispano-Suiza engine, which is used by the U.S. Army as an advanced training machine. This aeroplane won, in 1918, the Army competition for advanced training machines.
THE V.E.7 "BLUEBIRD" TRAINING MACHINE.
Type of machine Two-seater Biplane.
Name or type No. of machine V.E.7 "Bluebird."
Purpose for which intended Training.
Span 34 ft. 4 in.
Gap 4 ft. 8 In.
Overall length 24 ft. 5 3/8 In.
Maximum height 8 ft. 7 1/2 In.
Chord 4 ft. 7 1/2 in.
Span of tail 10 ft.
Engine type and h.p. 150 or 180 h.p. Hispano-Suiza.
Airscrew, diameter 8 ft. 8 in.
Weight of machine empty 1,392 lbs.
Performance.
Speed low down 106 m.p.h.
Speed at 6.500 feet 103 m.p.h.
Speed at 10.000 feat 97 m.p.h.
Speed at 15,000 feet 86 m.p.h.
Landing speed 48 m.p.h.
Climb.
To 6,500 feet in minutes 8 mins. 50 secs.
To 10,000 feet in minutes 15 mins. 15 secs.
To 15,000 feet in minutes 29 minutes.
Total weight of machine loaded 1,937 lbs.
W.Green, G.Swanborough The Complete Book of Fighters
LEWIS & VOUGHT VE-7 USA
Designed specifically as a tandem two-seat advanced trainer for the US Army, the VE-7 was the first product of the Lewis & Vought Corp. Founded on 18 June 1917 by Birdseye B Lewis and Chance M Vought, this was predecessor of the Chance Vought Corp (established in May 1922). A wooden two-bay equi-span biplane powered by a 150 hp Hispano-Suiza Model A engine, the VE-7 was completed in February 1918. It was adopted by the US Navy in October 1919, with the 180 hp Wright Hispano E-2 engine. A total of 129 was to be completed (69 by the Naval Aircraft Factory) and of these a substantial proportion emerged as VE-7G two- seat and VE-7S single-seat fighters. The former was a modification of the VE-7H unarmed single-float observation seaplane with controls transferred from rear to forward cockpit. A single fixed forward-firing synchronised 0.3-in (7,62-mm) Vickers gun was provided, together with a Lewis gun of similar calibre in the rear cockpit, and a wheel undercarriage was fitted. When provided with emergency flotation gear and hydrovanes, this type was designated VE-7GF. The single-seat fighter model was introduced in 1921. Forty were produced by Lewis & Vought and a further 24 by the Naval Aircraft Factory. These had the forward cockpit deleted and an armament of one synchronised 0.3-in (7,62-mm) Vickers gun. With wheel undercarriage, flotation gear and hydrovanes, it was designated VE-7SF, and with single main float and outrigger stabilising floats it was known as the VE-7SH. The VE-7S equipped the US Navy's first shipboard fighter squadron, VF-2, aboard the USS Langley. The following data relate to the VE-7SF.
Max speed, 117 mph (188 km/h) at sea level.
Time to 5,000 ft (1 525 m), 5.5 min.
Range, 290 mis (467 km).
Empty weight, 1,505 lb (683 kg).
Loaded weight, 2,100 lb (953 kg).
Span, 34 ft 1 3/8 in (10,40 m).
Length, 24 ft 5 1/8 in (7,44 m).
Height, 8 ft 7 in (2,62 m).
Wing area, 284.5 sqft (26,43 m2).
LEWIS & VOUGHT VE-9 USA
Essentially an improved VE-7, the VE-9 embodied comparatively minor changes, and these were mostly confined to the fuel system, a pair of interconnected tanks replacing the single tank of the earlier model. The VE-9 was powered by a 180 hp Wright Hispano E-3, and 21 were ordered by the US Navy in two versions; the single-seat VE-9 fighter with wheel undercarriage for shipboard use and the two-seat VE-9H unarmed observation float seaplane for catapult use from battleships and cruisers. The latter had modified vertical tail surfaces for improved water and catapult stability. The first VE-9 was delivered to the US Navy on 24 June 1922, the fighter version serving alongside the VE-7S aboard the USS Langley. Data for the VE-9 are as for the VE-7S.
 |
А.Шепс - Самолеты Первой мировой войны. Страны Антанты
|
| Разведчик/легкий бомбардировщик Воут VE-7 USAAS (1918г.)
|
 |
А.Шепс - Самолеты Первой мировой войны. Страны Антанты
|
| Истребитель Воут VE-7S USAAS (1919г.)
|
 |
А.Шепс - Самолеты Первой мировой войны. Страны Антанты
|
| Учебный самолет Воут VE-7G (1919г.)
|
 |
А.Шепс - Самолеты Первой мировой войны. Страны Антанты
|
| Морской разведчик Воут VE-7H U.S. Navy (1919г.)
|
 |
Jane's All The World Aircraft 1919 /Jane's/
|
| Side View of the Lewis & Vought V.E.7 Training Machine (Hispano-Suiza engine).
|
 |
Jane's All The World Aircraft 1919 /Jane's/
|
| Three-quarter Rear View of the Lewis & Vought V.E.7 (150 h.p. Hispano-Suiza engine).
|
 |
H.Cowin - Aviation Pioneers /Osprey/
|
| The first of the many Lewis and Vought VE-7s to be built. First flown in February 1918, this 150hp Hispano-Suiza A engined two seater had a top level speed of 106mph at sea level. Although too late to be useful for wartime pilot training with the US Army, who had taken eight of the envisaged 1,014 examples ordered at the end of the war, the VE-7 went on the become a major element of immediate post-war US naval aviation, with a total of 129 being used variously as trainers, armed two seat scouts and even single seat fighters, most versions having the option of fitting wheels or floats.
|
 |
G.Swanborough, P.Bowers - United States Navy Aircraft since 1911 /Putnam/
|
| A Vought VE-7, as produced for the Navy after the end of World War I.
|
 |
W.Green, G.Swanborough - The Complete Book of Fighters
|
| The two-seat VE-7G fighter variants of a trainer design.
|
 |
G.Swanborough, P.Bowers - United States Navy Aircraft since 1911 /Putnam/
|
| Vought VE-7S, the single-seat fighter version of the design, built by Lewis & Vought.
|
 |
Форум - Breguet's Aircraft Challenge /WWW/
|
|
|
 |
G.Swanborough, P.Bowers - United States Navy Aircraft since 1911 /Putnam/
|
| A Vought VE-7GF, built by the NAF, showing flotation gear and hydrovanes for emergency use.
|
 |
G.Loening - Takeoff into Greatness /Putnam/
|
| The Vought VE-9 two-seat trainer, Hispano motor.
|
 |
W.Green, G.Swanborough - The Complete Book of Fighters
|
| The VE-9 was, like the VE-7, built in single- (on photo) and two-seat fighter versions.
|
 |
G.Swanborough, P.Bowers - United States Navy Aircraft since 1911 /Putnam/
|
| A Vought VE-9H of Navy squadron VO-6 in December 1924.
|
 |
Jane's All The World Aircraft 1919 /Jane's/
|
| V-E-7 Plane with 150 h.p. Hispano-Suiza engine.
|
 |
Jane's All The World Aircraft 1919 /Jane's/
|
| V-E-7 Plane with 150 h.p. Hispano-Suiza engine.
|
 |
G.Swanborough, P.Bowers - United States Navy Aircraft since 1911 /Putnam/
|
| Vought VE-7
|
 |
W.Green, G.Swanborough - The Complete Book of Fighters
|
| The single-seat VE-7S fighter variants of a trainer design.
|